Cannabis growing methods in the tropics- Alchimia Grow Shop

Currently, the Internet is flooded with guides and tutorials for growing cannabis. Indoor, outdoor, hydroponic, best substrates, fertilizers, etc. The vast majority of guidelines apply to countries in the northern or southern hemisphere with temperate, continental, or Mediterranean climates, which experience all four seasons of the year. However, many growers live near the equator and these techniques and tips must be “adapted” for these tropical regions. In this article, we will analyze the tropical conditions and the most effective cultivation techniques best adapted to these latitudes.
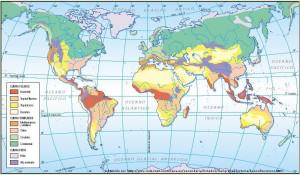
Tropical environment, definition and differences with other climates
The tropical climate is located between the tropics, near the equator. It is characterized by very warm temperatures, between 18 and 32 ºC, and very high humidity, between 70 and 90%. In some regions, rainfall is abundant throughout the year. The vegetation is highly developed and forms jungle areas.
In other drier regions, the vegetation is less abundant: it is the savanna. This climate extends over most of the Amazon, the Congo Basin, and regions near the coasts of the Gulf of Guinea, as well as the non-mountainous parts of the islands of Indonesia, New Guinea, and the Central Pacific islands. It is also found in Southeast Asia, as well as Mexico, the Antilles, Ivory Coast, and central Africa.
The natural photoperiod is approximately 12 hours of light and 12 hours of night throughout the year, with variations of up to 2 hours maximum, depending on proximity to the equator. The annual climate is characterized by 2 seasons: on the one hand, the dry season, with days that can exceed 40 °C in the shade without a great decrease at night, without rain or with little rain, and with a humidity of 60 -70%. On the other hand, we have the monsoon season, with intermittent heavy rains and high humidity (90%), with average temperatures of 20-30 °C.
Growing marijuana basing on latitude
Growth and flowering of cannabis depends directly on the hours of light to which the marijuana plant is exposed, so it is very important to be aware of the geographical area in the world where each strain is grown. Daylight hours differ in each area depending on the season. This article tells you when it is recommended to start growing marijuana based on the country and the region you are… We also give you some advice on suitable strains for each area, according to your preferences and needs.
As you can see, these conditions are really different from ours, inhabitants of the northern or southern hemisphere, who are used to living with four seasons a year and considerably lower temperatures and humidity.
Let’s then look at the cultivation methods used by experienced tropical growers.
Marijuana growing options in tropical environments
100% Outdoor
Given the temperature and humidity, the tropical climate is ideal for germination. This will not present problems, except during the peak of the dry season, where the temperature is too high and the humidity too low. For growth, the first problem is the constant annual cycle of light hours, which does not exceed 12-14 hours of light per day. Depending on when the seeds are germinated, the plants may take a long time to mature and will not develop much. They will begin to bloom after 7-8 months of growth, and the yield will not be very high.
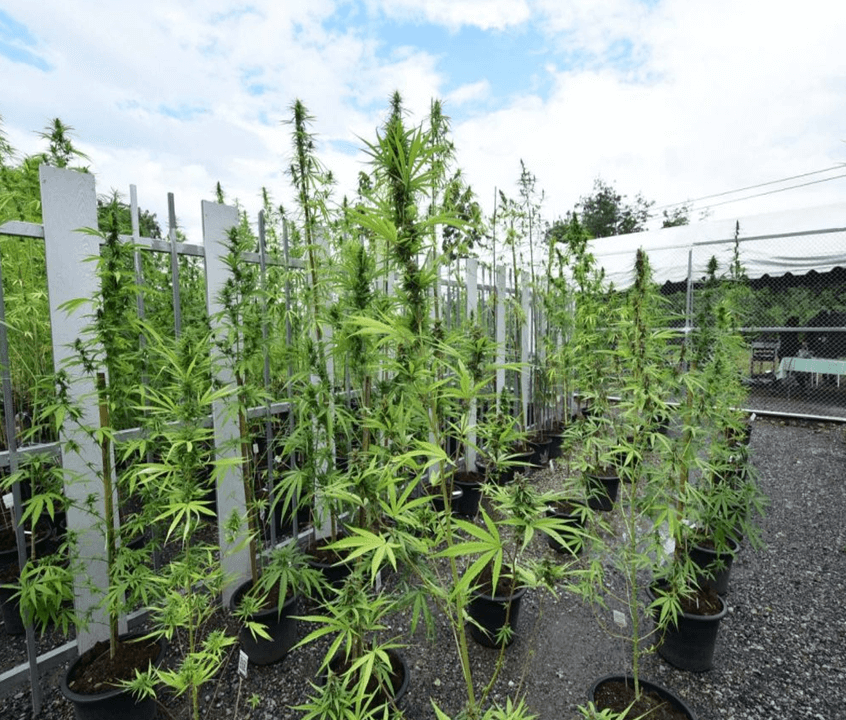

Autoflowering strains should be avoided completely, due to their need for a constant 18/6 light cycle. Thus, if grown outdoors in tropical environments, automatic plants will not exceed 30-40 cm in height with a maximum yield that will barely exceed a few grams of dried flower. In short, a waste of time and money…
If you decide to grow completely outdoors in a tropical country, choose 100% sativa varieties, preferably landrace and feminized, and if possible resistant to mold, especially botrytis.
For example, in the Ace Seeds catalog you can find many varieties suitable for these conditions. We highlight some:
In addition, it will be necessary to take into account the seasons; Germinating the seeds at the beginning of the monsoon season will cause your plants’ growth to occur during the rainy season, while flowering will occur at the beginning of the dry season, when the temperature begins to increase and the humidity to decrease.
Indoor growth / Outdoor bloom
This technique consists of carrying out germination and growth indoors, and then moving the plants outdoors to start flowering once they are sufficiently developed. In other words, the outdoor environment is used as a flowering room, where the plants that are ready to begin this stage are located.
This methodology is preferred by experienced tropical growers as it eliminates many problems: there is no longer a need for air conditioning and expensive indoor facilities. In addition, it allows continuous renewal of growing plants through cuttings. To give them a somewhat longer growth period once outdoors, many growers use a small LED light that provides enough lumens to provide a few extra hours of light per day so that their plants continue with a growth photoperiod until they grow. The grower decides that he wants to start flowering, at which point the artificial light will be removed.
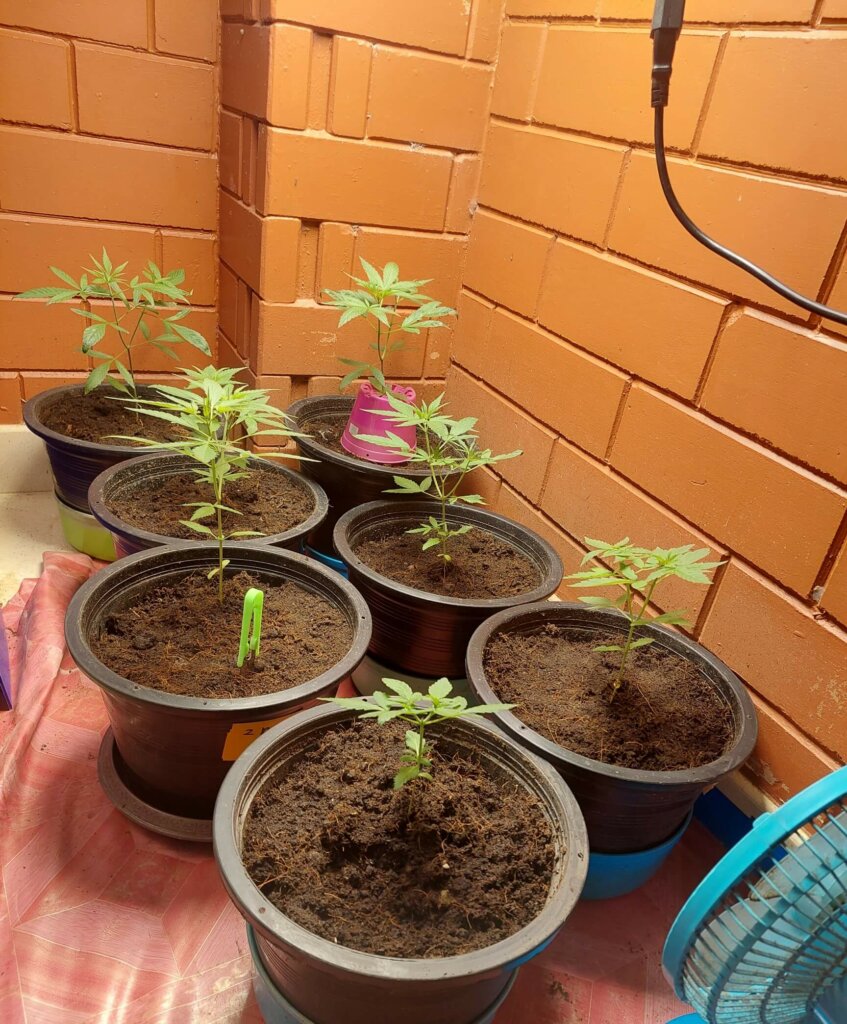

Germination and growth
In a tropical climate, to carry out germination and growth, the indoor growing setup is simple and requires little equipment, which may be of lower quality, since powerful lighting is only really necessary for flowering.
For lighting, a medium power LED panel, for example, the Mars Hydro 150 W lamp is perfect for covering 2m2 in growth, allowing you to place around 6-8 plants and some cuttings. HPS lights should be excluded because they increase the temperature, which is already quite high.
- For germination: the hot season should be avoided because the temperature is too high and the humidity is too low. Therefore, it is enough to germinate the seeds or install the cuttings in a corner of the house with a temperature that does not exceed 28 °C.
- During growth, there is little care to give, apart from 18h/6h lighting, adequate ventilation, basic pruning, such as topping, regular watering, and some growth nutrients. It is not really necessary to control the height of the plants, since they will be placed outdoors for flowering. Pots of about 8-10 liters are sufficient.
Moving plants outside for flowering
Ideally, start growth indoors during the rainy season with high humidity and low temperature, and then move the plants outside for flowering at the end of the rainy season, before the peak of the hot season. In this way, the plants will stretch during pre-flowering (stretch) at the end of the rainy season and the last month of flowering will take place in a mild climate, with little or no precipitation, without exceeding 30 °C during the day, 18°C at night, and 60-70% humidity. In order to achieve good acclimatization, ensure that your plants spend 2-3 days in the shade before placing them in their final place, now in full sun, and spray them with water if necessary to prevent them from dehydrating.
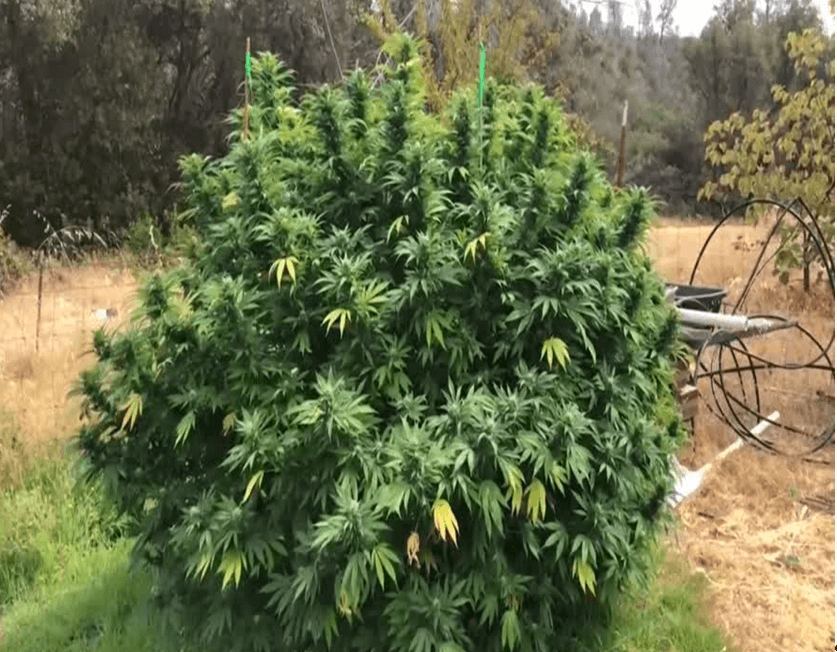

Plants can be transplanted into large 50L pots or planted directly into the ground, whenever suitable. To obtain maximum yields, it is preferable to opt for Sativa-dominant varieties, even 100%. Since Sativas have a longer stretch or pre-flowering period (5-8 weeks), this will allow the plants to triple or quadruple their size in the ground. The technique also works with Indica-dominant strains, although keep in mind that they will grow to approximately double their height, given the short 2-3 week stretch period before flower formation.
At harvest time, the temperature increases and humidity decreases; Perfect for manicure, drying and curing.
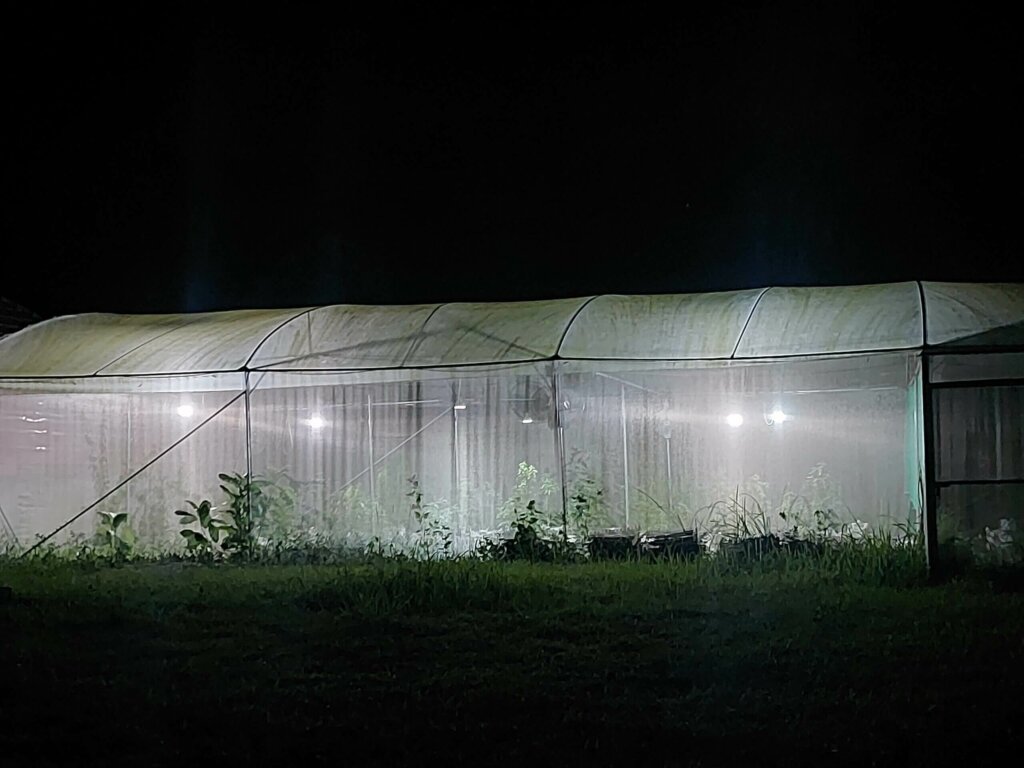
Growing cannabis outdoors with lighting
As we have already briefly mentioned, another increasingly common technique is to grow plants in an outdoor field, with lighting during the growth phase from dusk to providing 18 hours of daily light. When moving into flowering, simply stop illuminating the plants at dusk. However, it is recommended to germinate and develop the fragile seedlings indoors.

Marijuana growing tips in tropical countries
- Avoid in tropical countries: pieces of coconut, as they attract pests that devour the roots.
- Use neem oil or similar products: when plants are placed outdoors for flowering, either in pots or in the ground, it is recommended to water the soil and spray the leaves every 15 days with neem oil to eliminate larvae and eggs, as well as preventively.
- Against stress, especially that caused by excess heat: Biobizz Acti-Vera in foliar application is an excellent additive to combat stress.
As you just saw, growing cannabis in tropical environments is somewhat different from growing cannabis in countries in the northern or southern hemisphere. Although it is possible to grow alone outdoors or indoors, it seems that the combination of growing indoors and flowering outdoors has numerous logistical and economic advantages, something that most growers in these areas have already realized.
Don’t hesitate to tell us your favorite growing tricks for growing in these areas!
The articles published by Alchimiaweb, S.L. are reserved for adult clients only. We would like to remind our customers that cannabis seeds are not listed in the European Community catalogue. They are products intended for genetic conservation and collecting, in no case for cultivation. In some countries it is strictly forbidden to germinate cannabis seeds, other than those authorised by the European Union. We recommend our customers not to infringe the law in any way, we are not responsible for their use.