Cannabis and humidity- Alchimia Grow Shop

The relationship between cannabis cultivation and humidity levels is a fundamental factor that can influence the success and quality of the harvest in a decisive way. Cannabis, a plant known for both its medicinal and recreational properties, is extremely sensitive to environmental conditions, and humidity plays a crucial role in its development, whether we are talking about the growth or flowering phases.
In today’s article, we will explore in detail the importance of maintaining proper humidity levels when growing cannabis, the challenges that can arise when these levels are not properly managed, and best practices to ensure an optimal environment that encourages healthy growth and a copious, high-quality harvest. From germination to flowering, we’ll discover how humidity can become an ally or an enemy in growing this versatile plant, offering tips and strategies for novice and experienced growers alike. The balance between marijuana and humidity is an essential component in the growing process, and this article will help you understand it thoroughly.
Relative humidity, a key factor in cannabis cultivation
Environmental humidity or, in other words, the amount of water vapor present in the air, plays a crucial role in the development and health of plants, including, of course, the cultivation of marijuana. It affects plants in a variety of ways, and its level of influence can vary depending on the plant species and growth stages. Here are some ways that humidity affects plants:
- Transpiration and water absorption: Plants absorb water and nutrients through their roots and then transport it to the leaves, where photosynthesis occurs. Ambient humidity affects the speed of this process. When relative humidity is low, water evaporates more quickly from the leaves, which can lead to greater water absorption from the roots. On the other hand, in conditions of high humidity, the loss of water through evaporation is less, which can affect the absorption of fertilizers and nutrients.
- Development of diseases: Excessive levels of humidity can create an environment conducive to the growth of pathogens such as fungi and bacteria, whether in the aerial part (leaves and stems) or underground (roots) of the plants. This increases the risk of diseases that can damage the plants and decrease the quality of the harvest, a common problem in outdoor cannabis cultivation when rainfall is excessive in late summer or early fall.
- Plant structure: Humidity can also influence the morphology of plants. In high humidity conditions, plants may tend to stretch out in search of light, resulting in taller, thinner growth. On the other hand, in dry environments, plants can develop more compact and resistant structures.
- Temperature regulation: Humidity plays a role in regulating the temperature of plants. An environment with high humidity tends to have more stable temperatures, which can be beneficial at certain stages of growth. However, in high-humidity situations, plants may have difficulty releasing heat, which can be problematic in extreme heat.
- Pollination and reproduction: In some plants, humidity can influence the release of pollen and the pollination process. Changes in humidity can affect the effectiveness of pollination and fruit or seed formation.

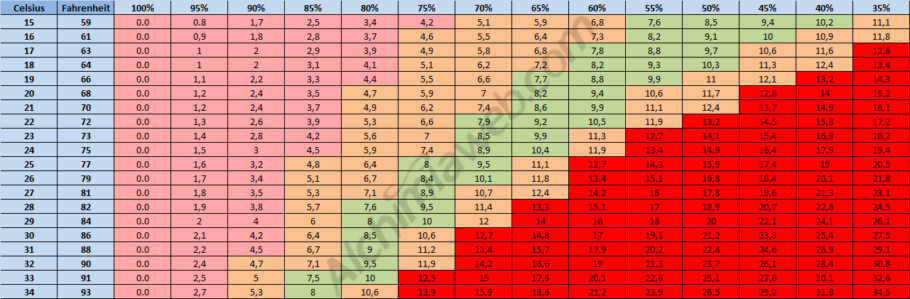
When growing cannabis, maintaining proper humidity levels is essential to ensure healthy growth and a high-quality harvest. Growers often adjust relative humidity based on the plant’s growth stages, maintaining higher levels during the vegetative phase and lowering it during flowering to avoid mold and mildew problems. However, the most experienced take into account the correct temperature values depending on the existing humidity and vice versa, thanks to the tables that indicate the vapor pressure deficit. We tell you in more detail below.
What is vapor pressure deficit and how does it work in cultivation?
Vapor pressure deficit or VPD is a concept used to describe the difference between the amount of water vapor that air can hold when it is saturated at a temperature and the amount of water vapor it actually contains at a given time. Although it sounds a bit technical, it can be explained more simply as follows:
Imagine a sponge, and that sponge represents air. When that sponge is completely soaked with water, it can’t absorb any more water, right? Now, if the air has all the water vapor it can hold at a certain temperature, we say that it is saturated. It’s as if the sponge is completely soaked and can’t absorb any more water.
But here’s the interesting part: sometimes, the air is not saturated and can still contain more water vapor. That difference between the amount of water vapor the air can hold when it is saturated and the amount it actually contains is called the “vapor pressure deficit.” So the vapor pressure deficit tells us how much room there is in the “sponge” of air for more water vapor. If the deficit is large, it means that the air is dry and can absorb more water. If it is small, it means that the air is close to being completely saturated and cannot absorb much more water vapor.
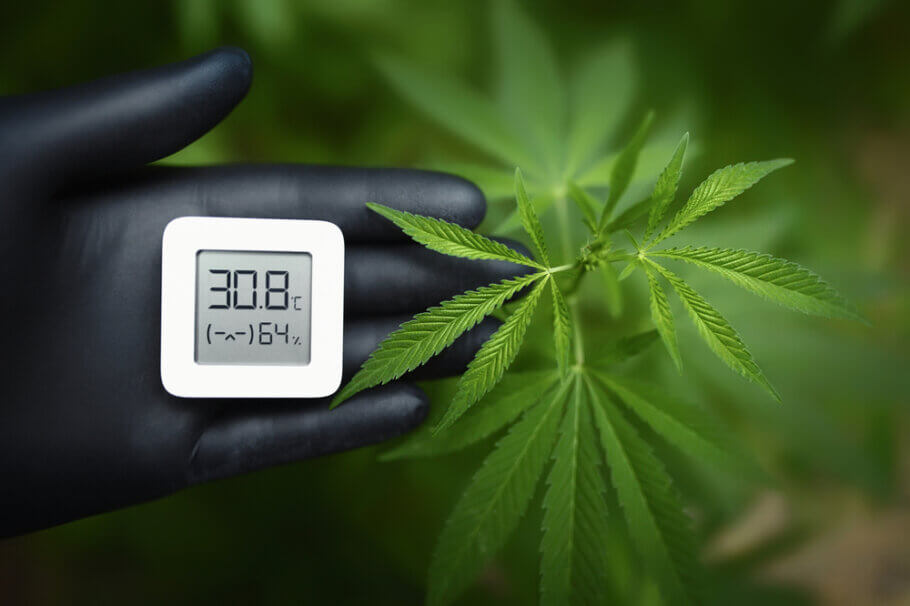

In short, VPD is a way of measuring how much moisture is in the air and how much more it can absorb. The larger the deficit, the drier the air, and the lower the deficit, the more humid it will be. This is important in many contexts, such as agriculture and plant breeding, as it can affect plant growth and water evaporation. You have much more information on this interesting topic as well as practical tables to know the correct relationship between humidity and temperature in this article:
Vapour pressure deficit (VPD) in cannabis cultivation
Temperature and relative humidity play an important role in indoor marijuana cultivation since much of the plant’s activity depends on these factors. Incorrect values of these two parameters will result in an invalid VPD (vapour pressure deficit), which will in turn result in poor plant development. In this article we explain how to properly adjust these values so our plants can enjoy a good climate for an amazing development.
Outdoor cultivation and humidity
Both indoor and outdoor cannabis cultivation can be negatively affected by excessive levels of humidity, although it is in the latter where these problems really tend to occur. Here are some of the most important risks that cannabis plants can face when grown in an environment with high humidity, whether we are talking about relative humidity in the air or excess humidity in the substrate:
- Mold and Mildew Development: Mold and mildew are one of the most serious risks. Under high humidity conditions, especially during the flowering phase, cannabis plants are prone to developing fungi such as powdery mildew and botrytis. These pathogens can destroy the crop by covering the flowers with white spores, ruining the appearance and quality of the cannabis.
- Loss of aroma and flavor: Cannabis plants that grow in humid environments may have difficulty developing their characteristic aromas and flavors. High humidity can dilute the aromatic compounds and terpenes that make each strain have its unique flavor profile and aroma.
- Slowed growth: Cannabis plants may grow more slowly in high humidity conditions due to difficulty absorbing water and nutrients. This can result in smaller, less productive plants.
- Root Damage: Constantly wet soil can lead to root problems, such as root rot, which negatively affects the health of the plant and its ability to absorb nutrients.
- Pest Attraction: Both high humidity and low humidity can attract insects and pests that can damage cannabis plants. This can include pests such as mites, whiteflies, and aphids.
- Reduced cannabis quality: In general, cannabis plants grown in high humidity conditions tend to produce lower quality buds, with less resin and THC, which decreases their value and effectiveness.
To mitigate these risks, outdoor cannabis growers often use techniques such as pruning to improve air circulation around plants and reduce leaf density, which helps prevent mold formation. They may also use antifungal treatments and closely monitor moisture levels. In extremely humid climates, some growers opt for greenhouses or roofed structures that allow greater control over environmental conditions.

Humidity, harvest, and drying of plants
The degree of environmental humidity can have a significant impact on the harvesting and drying process of plants, including cannabis. Here’s how humidity affects these critical stages of the growing process:
Influence of humidity on the harvest
Environmental humidity during harvest can influence the quality of the buds. A very humid environment can increase the risk of mold and fungus on the buds, which can ruin your cannabis harvest. This is why you will find that many outdoor growers wait for several straight days of good weather before harvesting their plants. On the other hand, a very dry environment can cause the leaves to dry out quickly, which can negatively affect the flavor and potency of the buds, something you’ve probably experienced if you’ve ever dried weed in a hurry and used methods that no expert would recommend. It’s okay…we’ve all done it!
Additionally, in high humidity conditions, plants can be significantly more difficult to handle during harvest due to the greater flexibility of the leaves and stems. This can make harvesting more complicated and laborious, costing you a lot of time. Always try to harvest your plants when they are not wet, and keep in mind that if you do not trim them when harvesting the plants will contain much more moisture and, therefore, will take longer to dry (which is not necessarily a bad thing, you will simply need more time to enjoy them).

Humidity and drying marijuana
Ambient humidity plays a crucial role in the rate of drying of plants after harvest. In a high-humidity environment, the drying process may be slower, which may increase the risk of mold development and affect the final quality of the cannabis. On the other hand, in a very dry environment, plants can dry out too quickly, which can also be detrimental.
Regarding the preservation of terpenes and cannabinoids, it is important to keep in mind that a drying environment with adequate humidity levels is essential to preserve these important compounds, which are ultimately what give each marijuana plant its unique flavor and effects. Drying too quickly or in extremely dry conditions can cause the loss of these valuable substances, ruining your efforts. The best when drying flowers is a degree of environmental humidity above 50%, so that the process is carried out evenly and without haste.
And another common problem during drying is a level of humidity that is too high, because as you already know, environmental humidity directly influences the formation of mold and fungi during the drying process. An environment with high humidity increases the risk of infestation, while a dry environment helps prevent it. Keep in mind that when placing plants to dry in your grow tent or drying room the humidity inside it will rise considerably!
To optimize the harvesting and drying process of cannabis plants, it is important to maintain a balance in environmental humidity levels. Growers often use drying rooms or controlled spaces where they can regulate humidity and temperature to create optimal conditions. Using adequate ventilation – as well as dehumidifiers or humidifiers – as needed is essential to achieve controlled drying and a high-quality harvest. Constant monitoring and attention to detail are critical to avoiding moisture-related issues during these critical stages of cannabis cultivation. We hope we have saved you a lot of headaches with this post!
Happy harvest!
The articles published by Alchimiaweb, S.L. are reserved for adult clients only. We would like to remind our customers that cannabis seeds are not listed in the European Community catalogue. They are products intended for genetic conservation and collecting, in no case for cultivation. In some countries it is strictly forbidden to germinate cannabis seeds, other than those authorised by the European Union. We recommend our customers not to infringe the law in any way, we are not responsible for their use.