What is anandamide?- Alchimia Grow Shop

In the complex framework of human biology, anandamide is presented as a key piece of our body, awakening the curiosity of scientists and doctors alike. Discovered in the last decade of the last century, this endogenous neurotransmitter molecule has awakened a vast field of study due to its amazing effects on the body and mind, which we will see in detail in today’s article.
From its ability to regulate mood and stress to its role in pain perception and appetite, anandamide appears to have a multifaceted reach in our biology, and in areas of no small importance precisely. Today we want to invite you to discover everything you need to know about this interesting molecule, exploring its origins, functions, and potential impact on our understanding of health and well-being, as well as of course its relationship with cannabis and phytocannabinoids.
What is anandamide?
Anandamide is an endogenous neurotransmitter chemical compound (that is, it originates inside our body) that belongs to the endocannabinoid family. It was discovered in 1992 by scientists Raphael Mechoulam and the NIMH (National Institute of Mental Health) in Bethesda, Maryland, USA. The name “anandamide” derives from the Sanskrit “ananda”, which means “happiness” or “bliss”, reflecting its effects on the nervous system. Although its first name was arachidonylethanolamide (AEA), fortunately, some brilliant minds decided to shorten the name and call it in a much easier way, anandamide. We thank you from the bottom of our hearts.
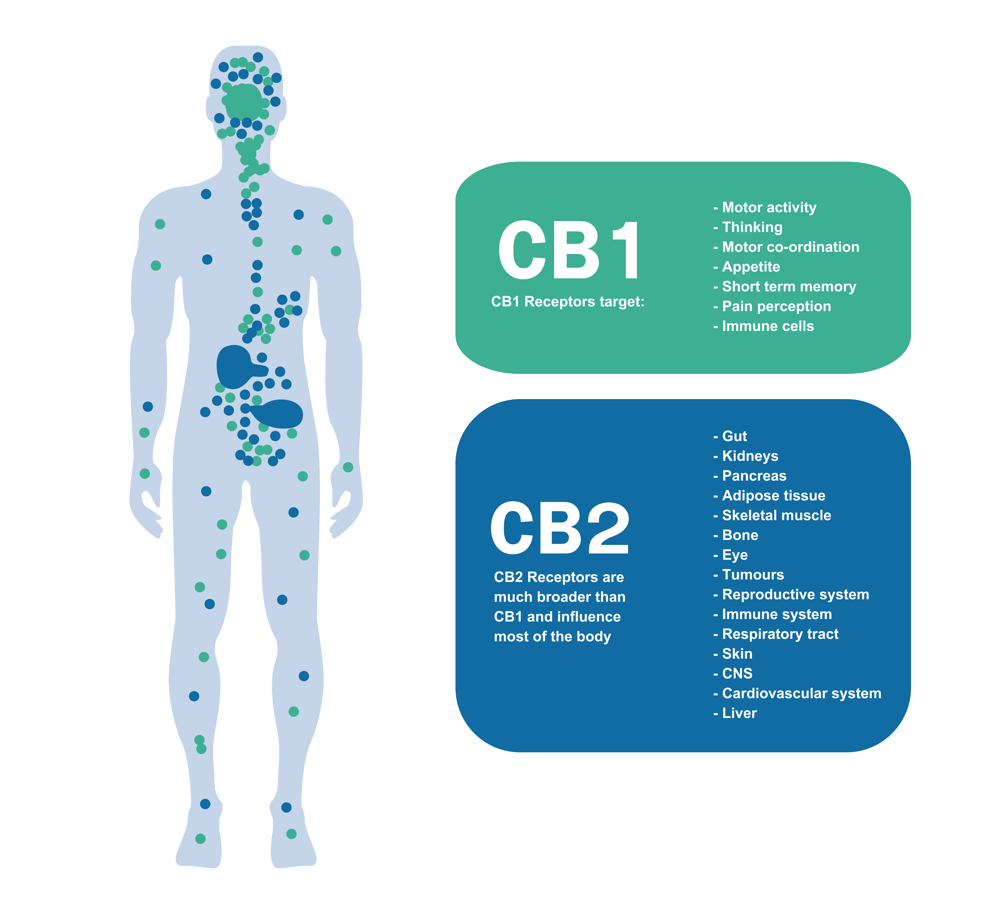
This compound is produced naturally in the human body and other animals (not in vain was it first identified in the brain of a pig) and plays an important role in the regulation of several physiological functions of no small importance, such as mood, appetite, memory, and pain perception. It acts on the cannabinoid receptors of the endocannabinoid system, especially the CB1 and CB2 receptors.
Anandamide is believed to contribute to emotional well-being and pain relief, and its role in the central nervous system continues to be studied in scientific research on mental health and pain treatment.
What is the endocannabinoid system? (ECS)
Do you know what regulates hunger, sleep, menstrual pain and also libido in our bodies? The endocannabinoid system is responsible for the balance of all these functions on which our health and emotional well-being depend so much. In this article, we explain what it is, how it works and what to do to keep it healthy.
Endocannabinoid system and endogenous cannabinoids
Broadly speaking, the endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a molecular signaling system present in the human body and in many other mammals. This system is made up of endogenous cannabinoids (naturally produced by the body), cannabinoid receptors, and enzymes that participate in the synthesis and degradation of cannabinoids.
Thus, unlike phytocannabinoids (produced by plants), endocannabinoids are chemical compounds produced naturally by the human body. They are signaling molecules that act as chemical messengers to regulate a variety of physiological and biological functions in the body, the two most studied endocannabinoids today being anandamide and 2-arachidonylglycerol (2-AG). These compounds are similar to cannabinoids present in the cannabis plant, such as THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol), but are produced internally by the body. Surprising, isn’t it?

How does anandamide affect the body?
Anandamide, being an endogenous neurotransmitter, plays a fundamental role in neuronal communication and in the regulation of various physiological functions. It mainly acts on cannabinoid receptors in the nervous system, especially the endocannabinoid system. By binding to these receptors, anandamide can modulate a variety of processes, including, as you have already seen, mood regulation, pain perception, appetite, memory, and immune function.
Its ability to influence these vital functions makes it a crucial element in the homeostasis of the human body, a very important vital process through which organisms regulate and maintain a constant internal balance, despite changes in the external environment. Additionally, anandamide has been found to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, suggesting its potential role in protecting against oxidative stress and inflammation.
What is the relationship between anandamide and cannabis?
Well, so far we have seen that anandamide is an endogenous neurotransmitter (endocannabinoid) produced naturally by the human body and that acts on cannabinoid receptors found throughout the nervous system and in other tissues of the body. Anandamide, in particular, is known for its role in regulating a wide range of important physiological functions, including homeostasis.
The relationship between this molecule and cannabis lies in the cannabinoid receptors. These receptors were initially identified in the 1980s as binding sites for active compounds present in cannabis, such as THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), the main psychoactive component of the plant. THC was found to have a similar molecular structure to anandamide, allowing it to bind to the same cannabinoid receptors and activate biological responses similar to those induced by anandamide naturally.
When cannabis is consumed, phytocannabinoids such as THC interact with cannabinoid receptors in the body, triggering a series of physiological and psychoactive effects. As you may know, these effects can include a feeling of euphoria, relaxation, altered time and space perception, as well as a reduction in pain and inflammation. In essence, when cannabis is consumed it acts as an external modulator of the endocannabinoid system, imitating and enhancing the actions of natural endocannabinoids such as anandamide.
Understanding the relationship between anandamide and cannabis has led to increased interest in the study of the endocannabinoid system and its therapeutic potential, which is always good news. Research is being conducted to explore how cannabinoids, whether derived from the cannabis plant (phytocannabinoids) or synthesized in the laboratory (synthetic cannabinoids), can be used to treat a variety of medical conditions, from mood disorders to neurodegenerative diseases and pain disorders.
Can the level of anandamide be increased?
The level of anandamide, like other endocannabinoids, can be influenced in various ways. Here are some strategies that can help you increase anandamide levels in the body:
- Physical exercise: Aerobic exercise has been shown to increase anandamide levels in the brain, which may contribute to the feeling of well-being associated with exercise.
- Balanced diet: Eating foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish, walnuts, and flax seeds, can promote anandamide production.
- Stress reduction: Chronic stress can decrease anandamide levels in the body. Practicing stress management techniques, such as meditation and deep breathing, can help reduce stress and maintain healthy anandamide levels.
- Natural Therapies: Some studies suggest that certain herbs and supplements, such as magnesium and CBD, can influence anandamide levels in the body. However, more research is needed to fully understand these effects.
- Sun Exposure: Moderate sun exposure can increase anandamide levels in the body. Sunlight activates the production of vitamin D in the skin, which in turn can increase the synthesis of anandamide.

It is important to note that the regulation of anandamide levels is complex and influenced by multiple factors. If you think that increasing them would help you in your daily life, it is always advisable to consult a health professional before making significant changes to your diet or lifestyle to improve these levels.
Conclusions
In conclusion, anandamide and cannabis are closely related in the human body thanks to the endocannabinoid system. Anandamide, as an endocannabinoid produced by the body itself, plays a crucial role in regulating a variety of important physiological functions, including mood, appetite, pain, and memory, thus contributing to the body’s homeostasis.
For its part, cannabis, containing cannabinoids similar to anandamide, can influence the endocannabinoid system by interacting with cannabinoid receptors in the body, which can have effects on various biological functions. While using cannabis for medicinal purposes may offer therapeutic benefits for some people, it is important to be aware of the potential risks and side effects associated with its use.
Ultimately, understanding the relationship between anandamide and cannabis can open new avenues of research and development of medical treatments that take advantage of the therapeutic potential of these compounds, with the aim of improving people’s health and well-being. From here, and as always, we hope that research does not stop and we soon have more information on how to take advantage of the properties of cannabinoids to improve our well-being.
We will continue to inform you!
References:
- Anandamide (arachidonylethanolamide), a brain cannabinoid receptor agonist, reduces sperm fertilizing capacity in sea urchins by inhibiting the acrosome reaction, Herbert Schuel, Elaine Goldstein, Raphael Mechoulam, Arthur M. Zimmerman, Selma Zimmerman
- Anandamide activation of CB1 receptors increases spontaneous bursting and oscillatory activity in the thalamus, M. Dasilva, K.L. Grieve, J. Cudeiro, C. Rivadulla
- The endocannabinoid system, anandamide and the regulation of mammalian cell apoptosis, Mauro Maccarrone, Alessandro Finazzi Agrò
- Role of the Endocannabinoid System in the Regulation of Intestinal Homeostasis, Hailey Cuddihey, Wallace K. MacNaughton, Keith A. Sharkey
The articles published by Alchimiaweb, S.L. are reserved for adult clients only. We would like to remind our customers that cannabis seeds are not listed in the European Community catalogue. They are products intended for genetic conservation and collecting, in no case for cultivation. In some countries it is strictly forbidden to germinate cannabis seeds, other than those authorised by the European Union. We recommend our customers not to infringe the law in any way, we are not responsible for their use.





